All About Linux
What is Linux?
Linux is a free open-source operating system that manages a computer's hardware and resources,like memory,storage and cpu.
Why linux?
It is a free,open source and secure platform with flexibility,customization and fast compared with other os.
What is Linux Boot process?
The Linux boot process has 6 levels:
BIOS: Basic input output system
-Perform integrity checks
-Search,load and execute the boot load program from cd-rom,hard drive,floppy
-In simple terms, the BIOS loads and executes the Master Boot Record (MBR) boot loader
MBR: Master boot record
-Located in first sector of bootable disk /dev/hda or /dev/sda
-It has 3 components 1.primary boot loader 2.partition table 3.mbr validation check
-It is responsible for loading and executing the GRUB boot loader.
GRUB:Grand Unified Bootloader executes kernel-It has multiple kernel images on your system
-Knowledge about file system
-Grub configuration file is /boot/grub/grub.conf
Kernel:Core of the operating system.
-Mounts root file system and executes /sbin/init program
-As it is the first program executed by kernel,its process id is 1
-initrd(initial RAM disk) is a used as a temporary root file system until kernel is booted.
Init:Looks at the /etc/inittab file to decide the Linux run level.
-0 – halt,1 – Single user mode, 2 – Multiuser, without NFS ,3 – Full multiuser mode , 4 – unused ,5 – X11 , 6 – reboot
Runlevel: When the Linux system is booting up, you might see various services getting started, depending on your default init level setting.
-Programs start with S are used during startup and K for shutdown.
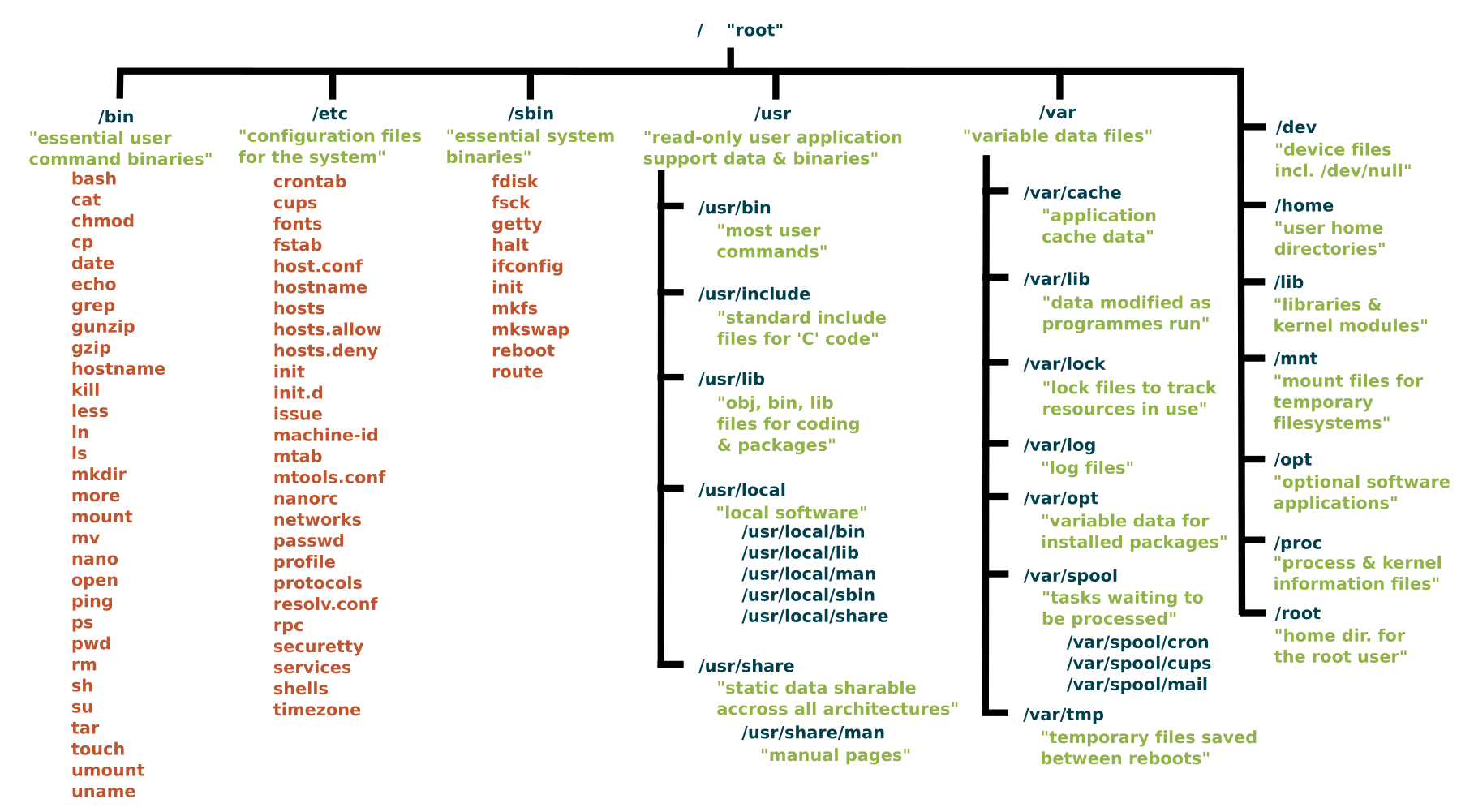
Top 50 linux Commands:
ls-Displays list of files or directories
pwd-print current working directory
cd-change directory ,cd ..-change directory to previous,cd ~-change directory to home
mkdir-create a new directory
mv-move or rename files
cp-copy a file
rm-remove file or directory
touch-creates a blank file
clear-clear the display
cat-Display the content of the file
ln - Create symbolic links (shortcuts) to other files
echo - Print any text that follows the command
less - Display paged outputs in the terminal
man - Access manual pages
uname - Gets basic information about the OS
whoami - Get the active username
tar - Command to extract and compress files in linux
grep - Search for a string within an output
head - Return the specified number of lines from the top
tail - Return the specified number of lines from the bottom
diff - Find the difference between two files
cmp - Allows you to check if two files are identical
comm - Combines the functionality of diff and cmp
sort - sort the content of a file while outputting
export - Export environment variables
zip - Zip files in Linux
unzip - Unzip files in Linux
ssh - Secure Shell command in Linux
service - Linux command to start and stop services
ps - Display active processes
kill and killall - Kill active processes by process ID or name
df - Display disk filesystem information
mount - Mount file systems in Linux
chmod -change file permissions,4-read,2-write,1-execute
chown - granting ownership of files or folders
ifconfig - Display network interfaces and IP addresses
traceroute - Trace all the network hops to reach the destination
wget - Direct download files from the internet
ufw - Firewall command
iptables - Base firewall for all other firewall utilities to interface with
apt, pacman, yum, rpm - Package managers depending on the distribution
sudo - Command to escalate privileges in Linux
cal - View a command-line calendar
alias - Create custom shortcuts for your regularly used commands
dd - Majorly used for creating bootable USB sticks
whereis - Locate the binary, source, and manual pages for a command
whatis - Find what a command is used for
top - View active processes live with their system usage
useradd and usermod - Add a new user or change existing user data
passwd - Create or update passwords for existing users
Linux File System: